What are the parts of a river?

Rivers shape the land surface and have an impact vertically as well as sideways on the landscape.
In geography we differentiate three parts of a river along its longitudinal profile, which is a graphical representation as a line of the course of a river, from source to mouth. Along the course, there are differences in river flow that depend on its velocity, which determines the river's erosion, transport and sedimentation.
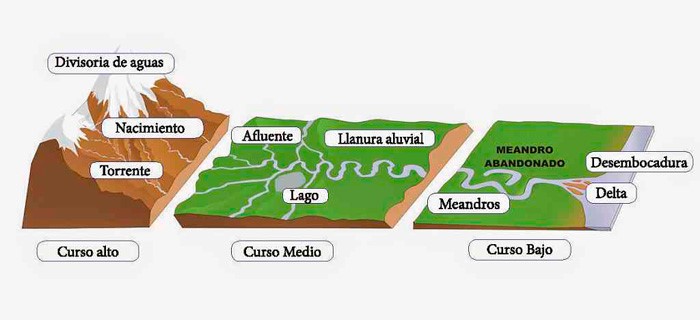
Diagram of the parts of a river (Source. Epicentro geográfico).
1 . Upper course
The upper course of a river is where we find its source (often in mountainous regions of the river basin); here it flows down steep slopes as a fast flowing stream. In the upper course, erosion and transport processes prevail over sedimentation.
In this part of the course, erosion of the river bed leads to V-shaped valleys, gorges and canyons, where water has a high oxygen content. The most common features we find in this part of the river are waterfalls, rapids, potholes, etc.
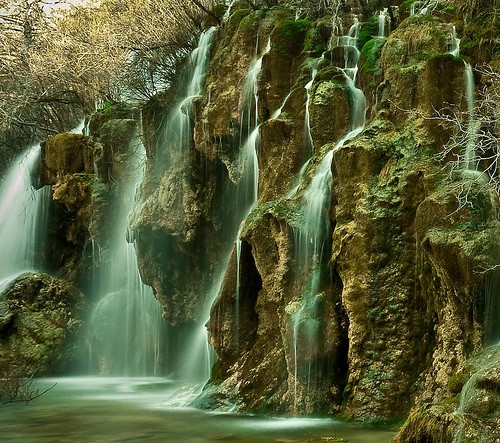

Waterfall at the source of the Cuervo river, Spain (Source: Wikipedia).
2 . Middle course
In the middle course of the river the water velocity slows down in comparison with the upper course. The river channel widens, discharge increases, and the gradient becomes less steep. Transport and sedimentation processes prevail over erosion.
Flat and wide valleys are formed, known as alluvial plains or floodplains. The channel may be anastomosed and meandering. In meandering courses, erosion occurs on the outer, concave bank, and sediments are deposited on the inner, convex bank. The valley becomes wider as the river meanders.

Image of a meander in the Amazon river (Source: Lifeder).
3 . Lower course
The lower course is the final part of a river, where the gradient and the water velocity decrease. The river no longer has erosion capacity, and the processes that predominate are sedimentation and transport of very fine material.
In this part of the course, the discharge may spread over the floodplain during high water periods. Transported sediments are collected in these large plains, including nutrients that fertilise the river valley. These fertile river valleys are often used to grow irrigated crops, taking advantage of the soil's fertility and the availability of water. Sometimes there are settlements in these valleys, exposed to hazards from high water flows or floods. In this part of the river's course, groundwater aquifers are often recharged and sometimes tributaries join the main channel.

The Segura river valley, Spain. (Source: Wikipedia).
At the mouth of the river we may find two different types of landforms:
Delta: formed by the deposition of large amounts of sediment as the water velocity slows down. Sediments block the mouth of the river as it flows into slow-moving sea water.
The Ebro river delta, Spain (Source: La Vanguardia).
Estuary: water flows out of the river's mouth at high velocity, so sediments quickly go into a fast-moving sea.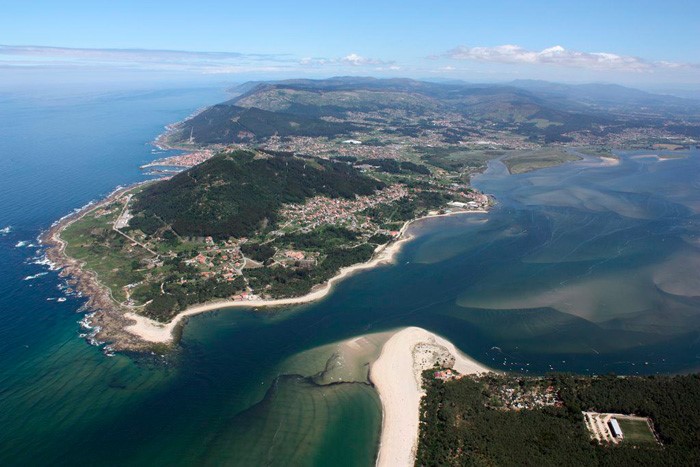
Miño river estuary, Spain (Source: Turismo A Guarda).









