The 10 Animals With the Highest Populations on the Planet
Our planet is brimming over with life. The diversity of animal life on Earth is staggering. Over 2.1 million animal species have been described, but zoologists estimate that millions more have yet to be discovered. Some of these animal species are critically endangered, but others exist in quantities that are difficult to comprehend. While the exact numbers of these animals are impossible to ascertain, here are ten of the animals that are believed to have some of the highest population numbers on the planet.
Crustaceans
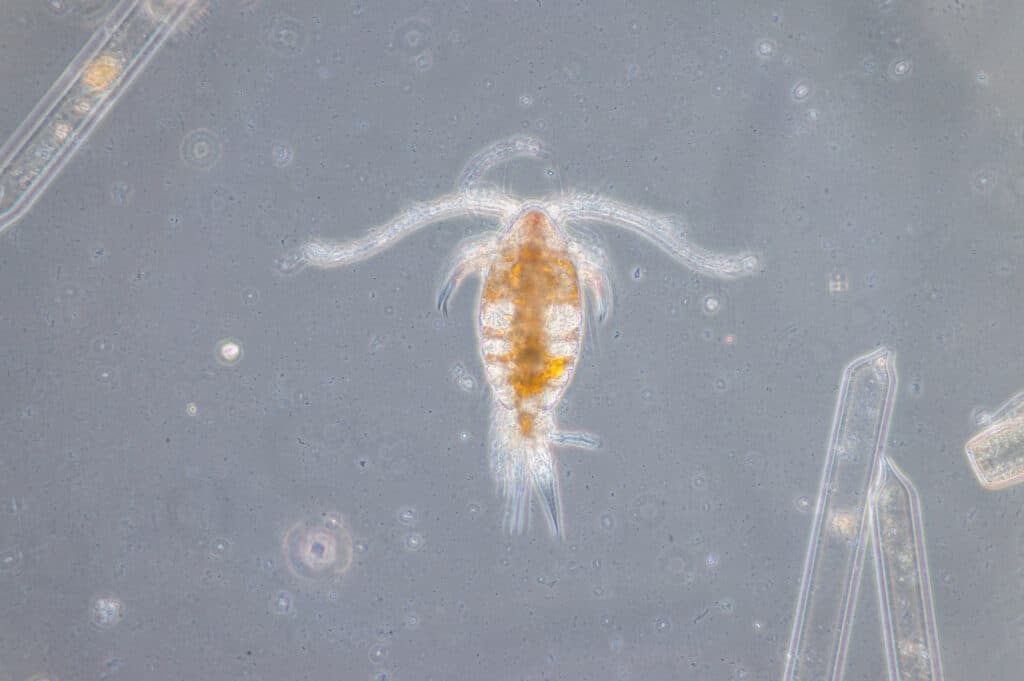
1. Copepods
©iStock.com/tonaquatic
Crustaceans are mostly water-dwelling arthropods. Lobsters, crabs, and shrimp are all crustaceans. One group of small crustaceans may be the most populous animal on the planet.
Copepods live in virtually every freshwater and saltwater environment. There are approximately 12,000 species of copepods that have been identified. These small creatures typically measure only a few millimeters
Copepods feed on bacteria, algae, and phytoplankton. They are important prey for many aquatic creatures, from tiny fish to huge whales.
While exact numbers will never be known (no one is organizing a copepod census anytime soon!), there are an estimated 1,347,000,000,000,000,000,000 copepods in Earth’s waters today!
2. Krill
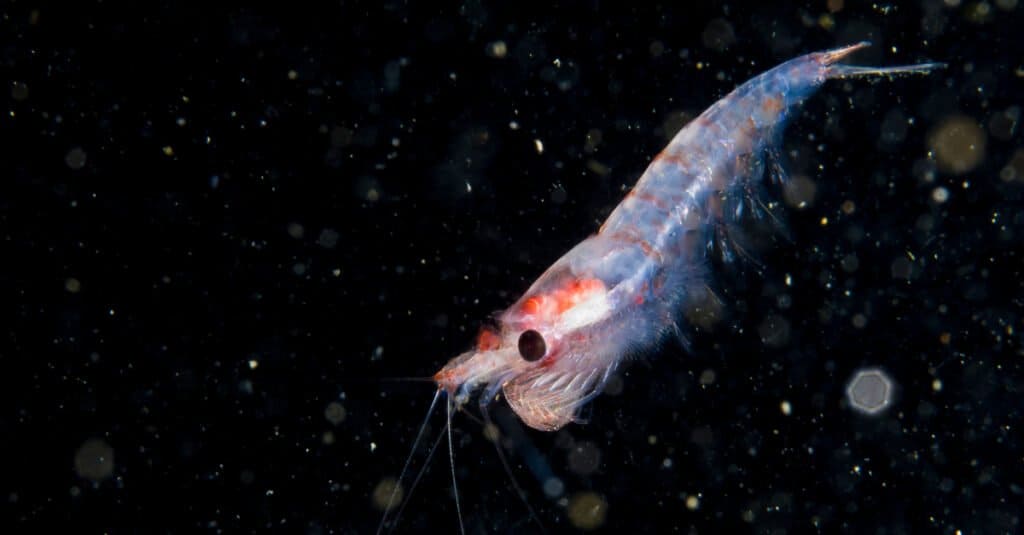

©RLS Photo/Shutterstock.com
Krill are another crustacean that exists in mind-boggling numbers. Antarctic krill, in particular, are estimated to number over 500 trillion. These crustaceans feed on phytoplankton and are the bedrock of the food chain in their ecosystem. Fish, penguins, and whales all feed on these krill.
Insects
3. Ant
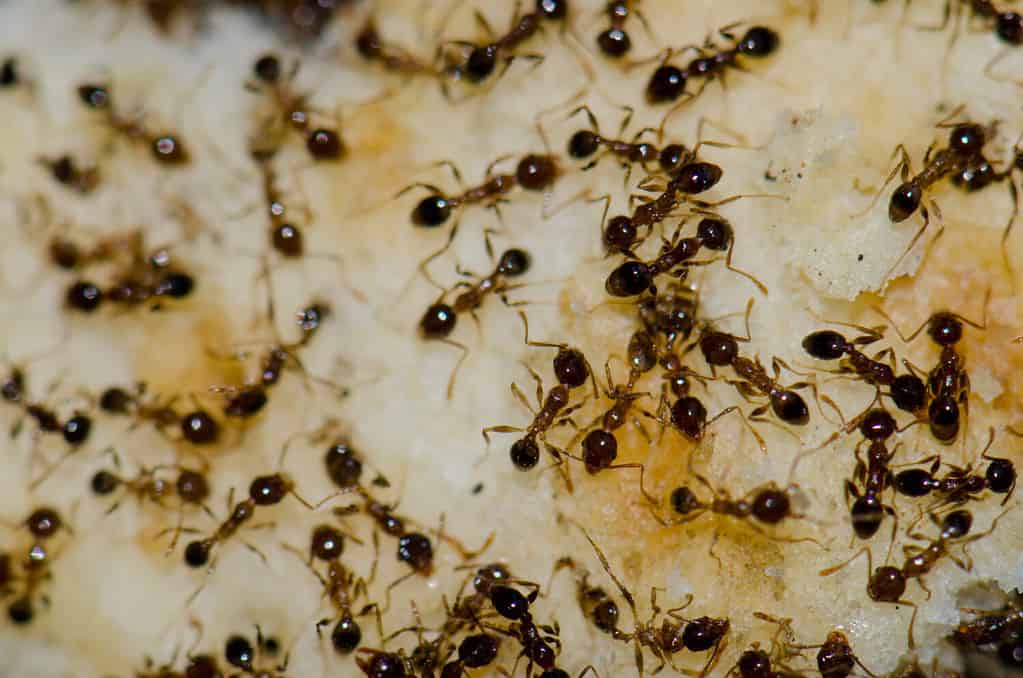

©Victor Suarez Naranjo/Shutterstock.com
The most populous insect on the planet is unquestionably the ant. These small invertebrates are found on every continent except Antarctica. Over 10,000 species of ants have been identified. The world’s ant population is estimated to be around 20 quadrillion. That is 20 million billion, or 20,000,000,000,000,000. Some experts even believe that the estimate of 20 quadrillion ants on Earth may be too low! The combined biomass of the world’s ants exceeds that of every wild bird and non-human mammal combined.
The Argentine ant may be the most populous of the world’s thousands of ant species, though we can’t be certain. These ants are native to South America but have been inadvertently transported all over the world since they stow away in cargo shipments. Argentine ants live in massive colonies that can stretch hundreds of miles. There are many breeding females instead of just one queen in these colonies, meaning these ants reproduce prolifically.
Fish
4. Bristlemouth
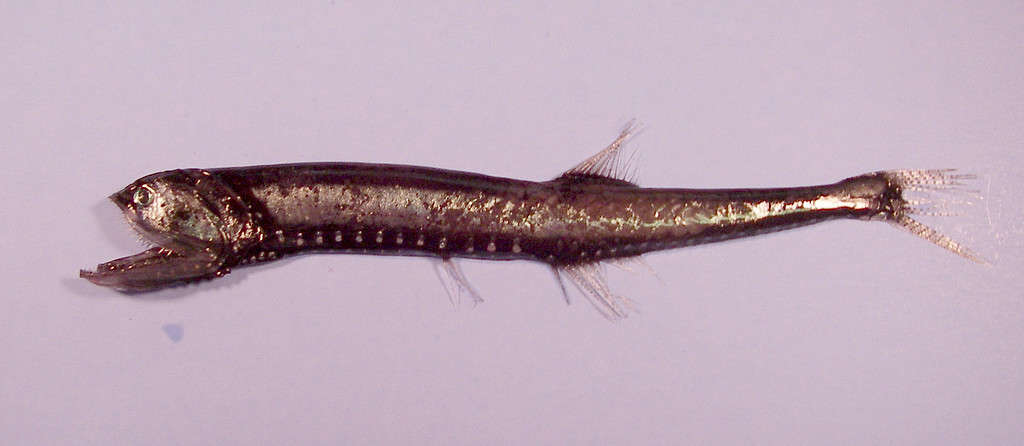

©SEFSC Pascagoula Laboratory; Collection of Brandi Noble, NOAA/NMFS/SEFSC. / Public domain – License
There are 34,300 species of fish that have been described. Out of those tens of thousands of species, one fish is thought to outnumber all the others: the bristlemouth (sometimes known as lightfish). There are trillions, possibly quadrillions of these fish swimming in the depths of the world’s oceans.
Bristlemouths are tiny bioluminescent fish. Significant sunlight only penetrates to about 650 feet in the ocean. The tiniest glimmers of light can sometimes be detected up to half a mile deep, but only under perfect conditions. However, bristlemouths live at depths up to three miles. Their environment is pitch black, but these fish have light-emitting organs along their sides called photophores.
The bristlemouth is named for its bristle-like teeth that it uses to capture its prey. The fish typically feeds on crustaceans, zooplankton, and smaller fish. In turn, bristlemouths are important prey for larger deep-sea fish.
Since the bristlemouth lives at such extreme, inaccessible depths, we know little about it including its actual population numbers. However, bristlemouths likely outnumber every other fish in the world. Not only that but they are also believed to be the most populous vertebrate on Earth today.
Amphibians
5. Frog
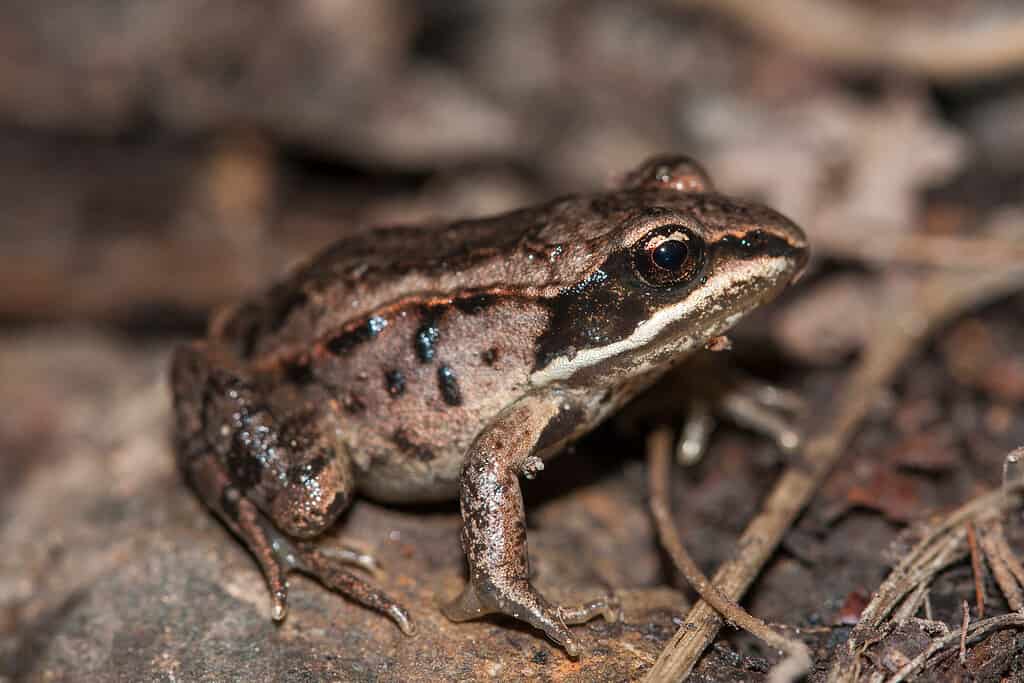

©Viktor Loki/Shutterstock.com
There are currently 8,689 known species of amphibians today, but new species are discovered every year. The world’s most populous amphibian species is not known, but it’s almost certainly a frog.
Some possible candidates for the world’s most populous amphibian include the common frog (Rana temporaria) which can be found throughout Europe. The wood frog (Lithobates sylvatica) is also a possibility. This frog lives in North America, even as far north as the Arctic Circle. The African clawed frog (Xenopus laevis) is another contender. The population of these frogs became artificially inflated when scientists bred them for use in human pregnancy tests in the mid-twentieth century.
While the exact population numbers of these frogs remain a mystery, all of them have thrived, at least in part because of their varied diet. Generally speaking, they will eat anything they can catch. They are also adaptable to various climates.
Birds
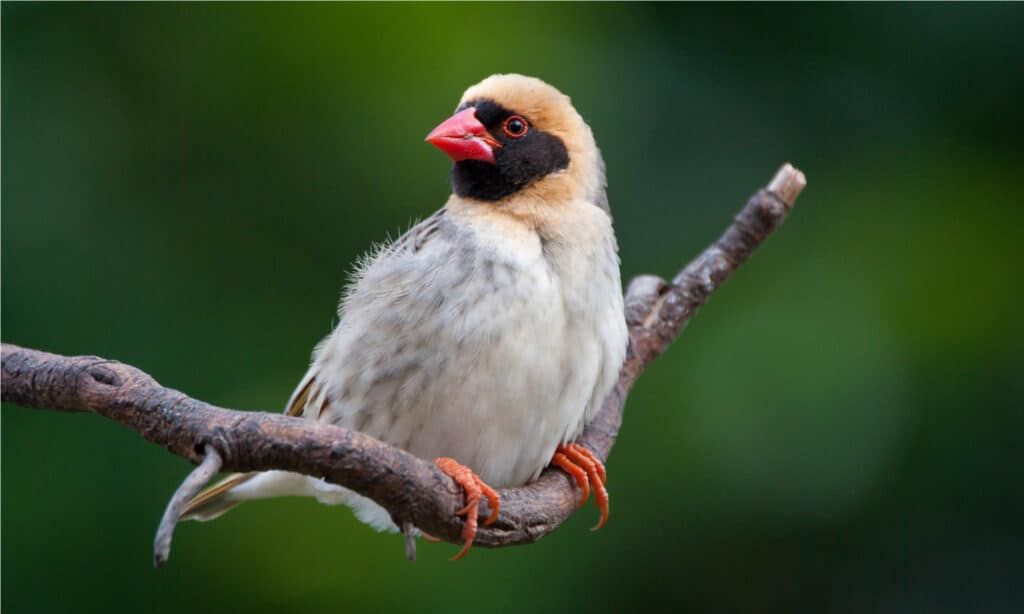
6. Red-billed quelea

©Linn Currie/Shutterstock.com
There are more than 10,000 species of birds that have been described, but one wild bird is more numerous than all the others. The red-billed quelea (Quelea quelea) has a range that covers roughly two-thirds of Africa. No one knows how many of these birds exist today, but the lowest estimate is around 1.5 billion. Some estimate that there may be as many as 10 billion!
These birds resemble finches and sparrows, but African farmers certainly don’t view them as harmless songbirds. These seed-eating birds form flocks of thousands, even millions, that can devastate entire grain harvests. These small birds are among the most dreaded agricultural pests in Africa.
Red-billed queleas are a food source for many different predators. However, because these birds often breed multiple times per year, their population numbers continue to grow despite the high rate of predation.
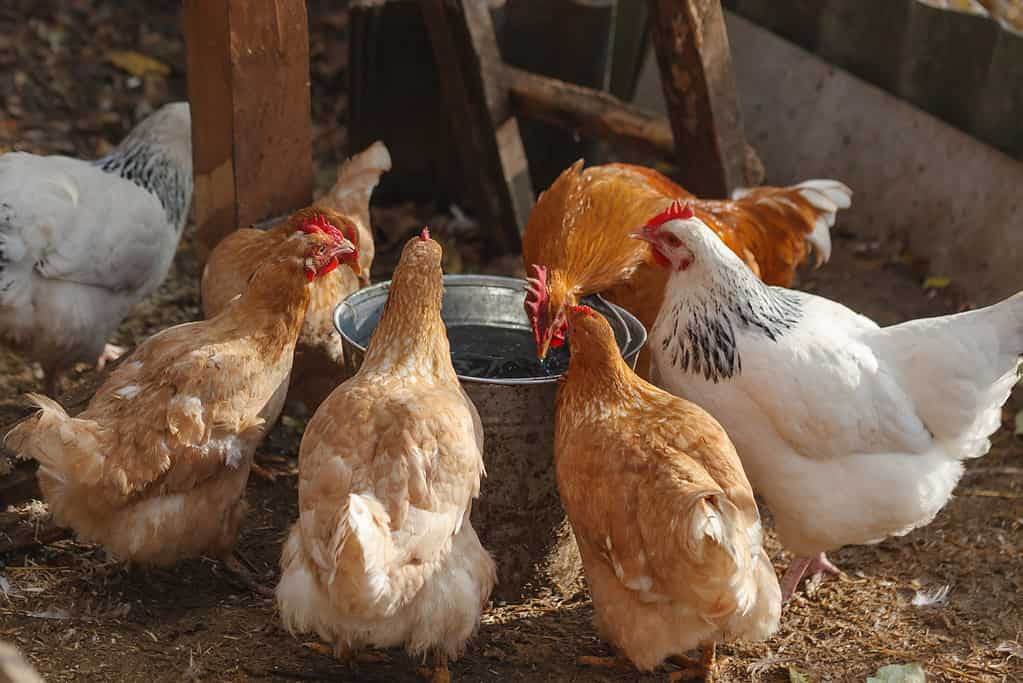
7. Domestic Chicken

©Olesya Andreeva/ via Getty Images
A visit to a poultry farm is all you need to do to see the most populous bird in the world. Domestic chickens outnumber the wild red-billed quelea and probably every other bird on Earth. Some estimate the number of domestic chickens to be over 33 billion. It’s not an apples-to-apples comparison, though, since domestic chicken breeding is managed and optimized through human farming practices.
Mammals
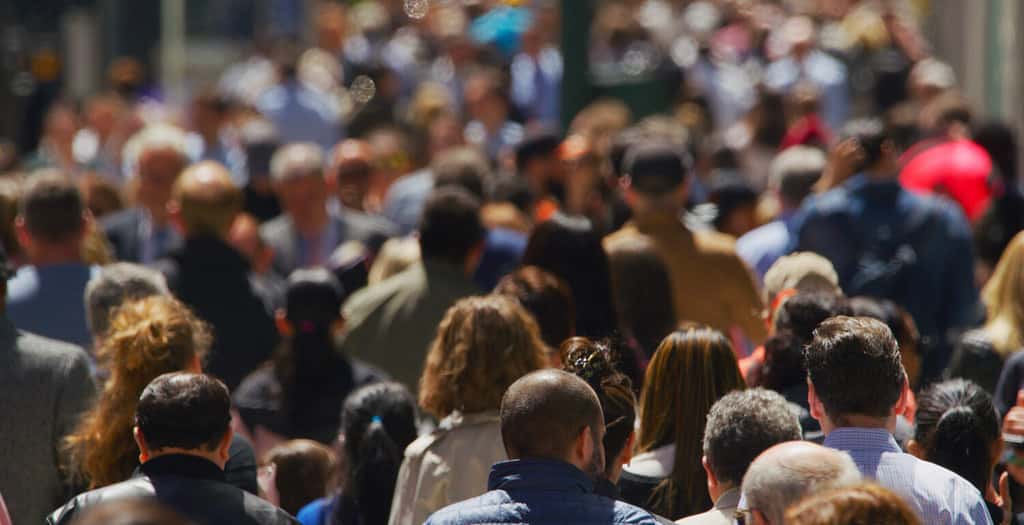
8. Humans
The most populous mammal on Earth might be human beings. The United Nations estimated that the population of humans on Earth surpassed eight billion for the first time in November 2022.

©blvdone/Shutterstock.com
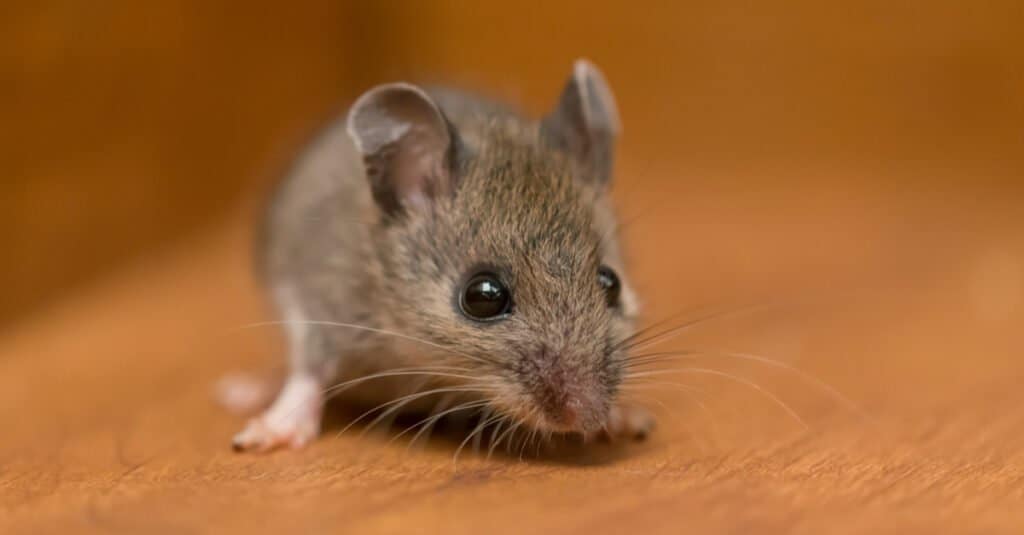
9-10. Rats and Mice

©MainelyPhotos/Shutterstock.com
There are a few mammals that might surpass the number of humans on Earth, such as the house mouse (Mus musculus) or the brown rat (Rattus norvegicus). The proliferation of rats and mice is inextricably linked to the growth of the human population. These rodents often find food and shelter through human activities. As with most of the animals on the list, the exact number of mice and rats is unknown.
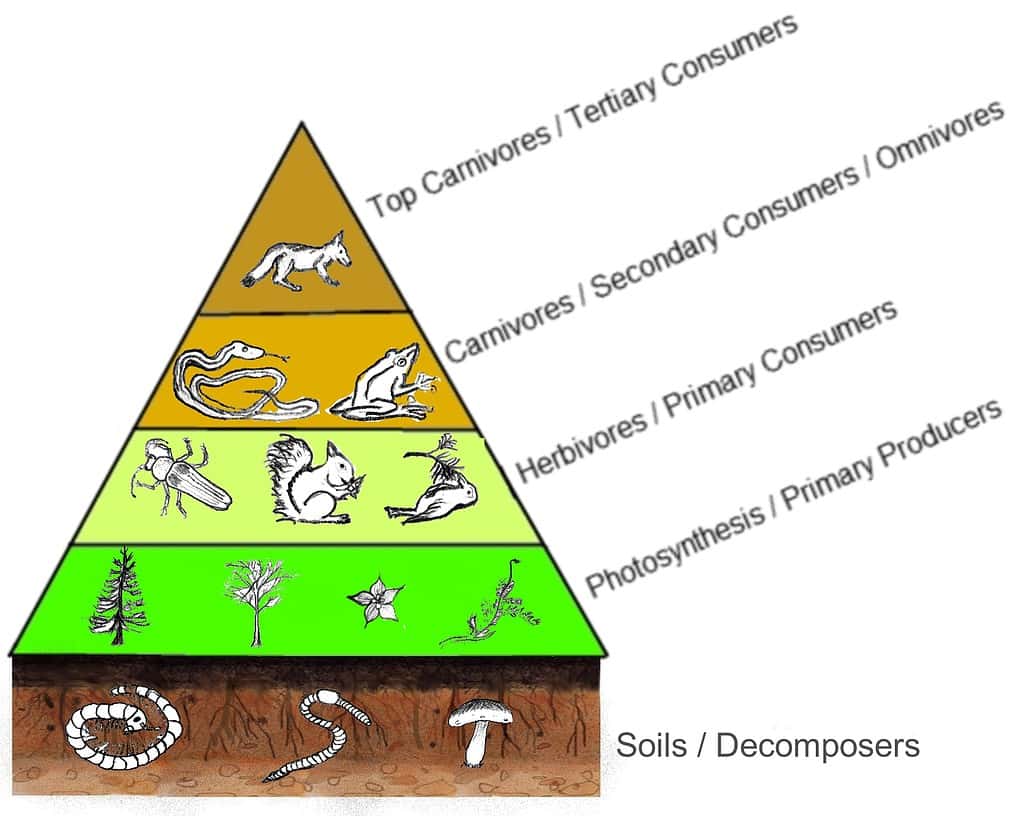
Trophic Pyramid
©Thompsma / CC BY-SA 3.0 – License
When examining the list of the most populous animals on Earth, one trend clearly emerges. With the exception of humans, every animal on the list is near the bottom of the trophic pyramid (also known as the food chain). The bottom of the pyramid consists of plants that use photosynthesis for energy. Those plants are consumed by herbivores, which are then consumed by carnivores. Only a fraction of the energy from each trophic level is passed on to the next higher level, so there are fewer animals in each subsequent level. That is why there are no apex predators on the list of the world’s most populous animals.









