Can Fish See in the Dark? This Is What Experts Say
In many places, the ocean is deep and dark. Some fish have adapted to live in those places by producing light, like anglerfish, and others have other methods. But you may be wondering, can fish see in the dark? Whether fresh or saltwater, we’re here to cover what experts say about the matter.
Extra Rod Cells
Fish can’t quite ‘see in the dark’, but they have much stronger vision in low light conditions than humans do. However, it depends on each species. Many deep-sea species of fish have evolved to have high-sensitive vision. They can see in almost total darkness because of this.
Almost all fish have better night vision than humans, which is due to the extra rod cells at the backs of their eyes. The collection of extra rods is called a multibank retina, and it’s made of as many as 28 light-sensitive opsins. Fish that live in deeper and darker conditions generally have evolved to have closer to 28, while fish living in lighter conditions may have less, which is more similar to human vision.
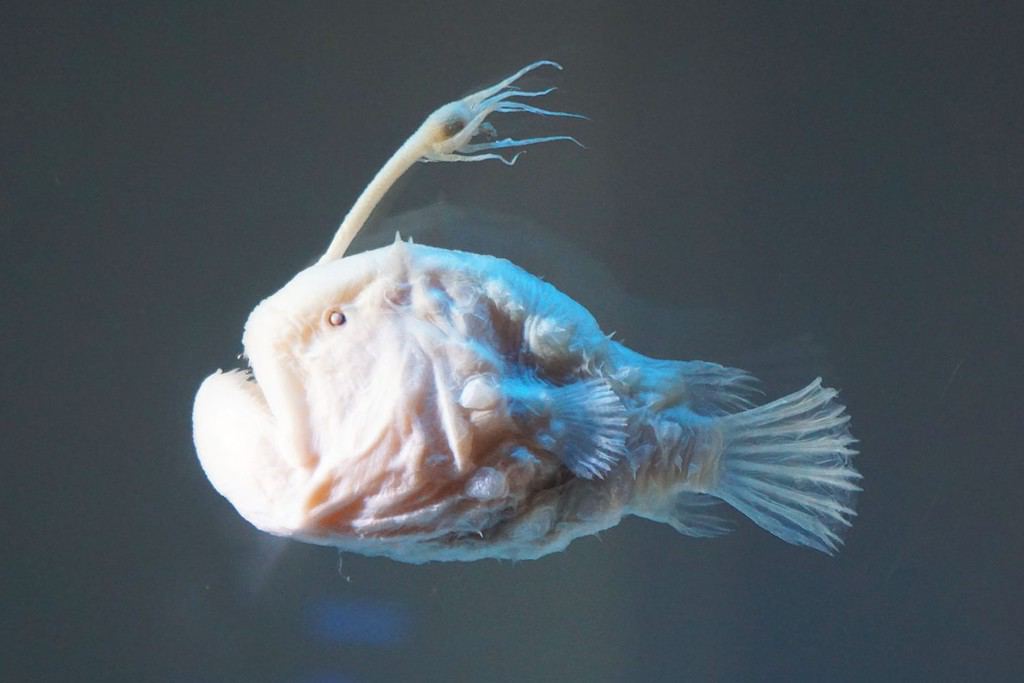

Female
anglerfish
can produce light, but both sexes can see well in the dark conditions they live in.
©panparinda/Shutterstock.com
Seeing By Feeling
Even when it’s dark and fish can’t see, they can understand the world around them by feeling. They have pressure-sensitive organs on both sides of their bodies that feel any slight changes in water pressure. When another fish moves by them, they can feel which direction the pressure changes, and know that there is something nearby.
Using Bioluminescence
Because fish species that live in deep parts of the ocean have adapted to their surroundings, they can see using other light sources. One of those sources is the faint bioluminescence that other fish, bacteria, octopuses, and shellfish emit. You may recognize bioluminescence as the glowing green or blue eye color you may have seen on fish, or a faint glow to their scales. This is usually present in fish that live in deep water.
While the shiny light of a fish’s eye doesn’t sound like much to you or me, it’s enough to light up a deep underwater world. Studies on deep sea creatures have shown that they produce amino acid sequences that can detect other wavelengths of light like those given off by bioluminescence.
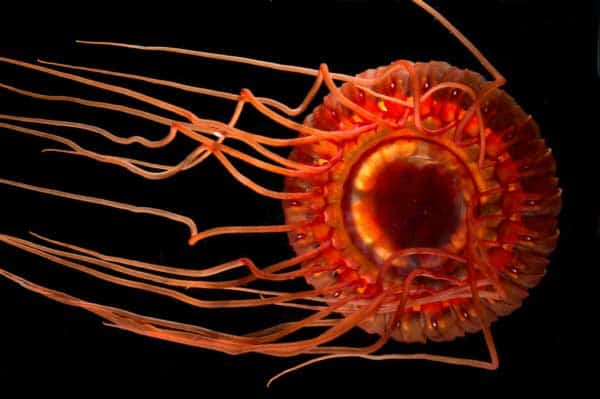
Atolla
jellyfish
are bioluminescent and emit a blue-green light. Some fish have adapted to use this light to see.
©NOAA Ocean Explorer_Operation Deep Scope 2004: Eye-in-the-Sea Bioluminescence/CCBYSA2.0 – License
Aquarium Fish and Shallower Species
When it comes to fish like bettas and goldfish, these species cannot see in the dark. They have limited night vision, similar to humans. Goldfish and betta fish follow sleep patterns like ours too, resting most of the night with a few mid-day ‘naps’. Species like these and other common aquarium fish cannot usually see in the dark any better than we can.
The photo featured at the top of this post is © UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering / CC BY 2.0 / flickr – License / Original









